- What does the inside of a catalytic converter look like?
- What precious metals are in a catalytic converter?
- What kind of catalytic converter do I have?
- How to Recycle My Catalytic Converter?
- How to identify a catalytic converter?
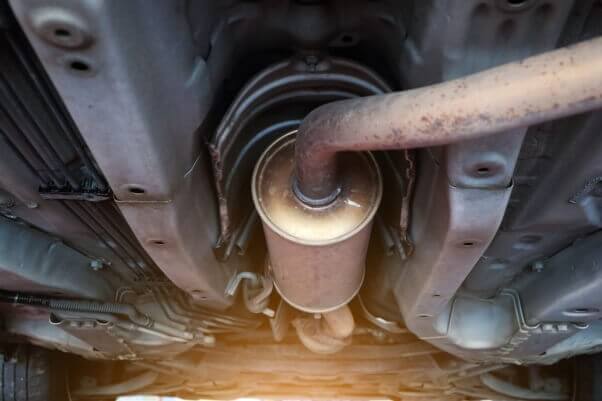
Catalytic converters are crucial emissions control devices in vehicles, tasked with reducing harmful pollutants. Identifying these converters is key due to their high scrap value, which you can benefit from via recycling. In this catalytic converter identification guide, we'll illustrate how to recognize catalytic converters, delve into their value, see what’s inside, and provide insights on actions to take to properly utilize used “cats”.
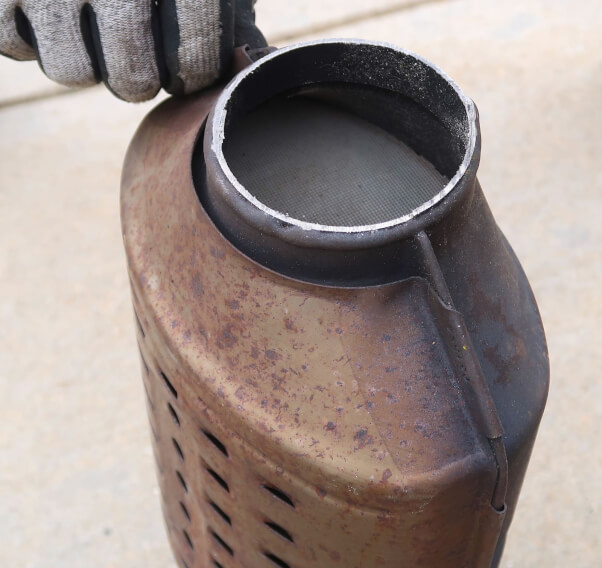
What does the inside of a catalytic converter look like?
Within a catalytic converter, a honeycomb-like structure made of ceramic or metal houses catalyst elements coated on its surface. These catalysts are precious metals that are hard to develop in nature purposing to boost redox chemical reactions to convert harmful gases like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons into benign substances: Nitrogen, water, and Carbon dioxide. The inner structure increases the surface area for efficient conversion. Meanwhile, the outer shell, typically made of stainless steel, protects the catalyst and ensures heat retention. The composition and design vary, but all work toward the same goal of reducing harmful emissions from vehicles.
What precious metals are in a catalytic converter?
Catalysts are made of platinum, palladium, and rhodium. Each of those elements plays a certain role in order to clean the exhaust pollutants. They are all very similar as they take place in the platinum group of the periodic table.
- Platinum (Pt): This catalyst aids in oxidizing carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into less harmful gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor. Its role is pivotal in converting these pollutants into more benign substances.
- Palladium (Pd): Acting as a catalyst, palladium assists in the conversion of nitrogen oxides into nitrogen and oxygen molecules, contributing significantly to the reduction of harmful emissions from vehicles.
- Rhodium (Rh): Rhodium plays a vital role in further reducing nitrogen oxides into harmless nitrogen and oxygen compounds. Its catalytic properties ensure the efficient conversion of these pollutants, enhancing the converter's effectiveness.
Certain catalysts (catalytic converters) may contain different values of those elements. It depends on types, emission control standards (Euro 3-6), and car brands.
What kind of catalytic converter do I have?
Catalytic converters come in several types, each designed to meet specific emission reduction needs and engine configurations. The main varieties include:
- Two-Way Catalytic Converters: Initially introduced in older vehicles, two-way converters primarily target two harmful emissions: hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide. They utilize platinum and rhodium catalysts to facilitate oxidation and reduction reactions, converting these pollutants into carbon dioxide and water.
- Three-Way Catalytic Converters: Found in most modern gasoline-powered vehicles, three-way converters aim to address three major pollutants: nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrocarbons (HC), and carbon monoxide (CO). Utilizing a combination of platinum, palladium, and rhodium catalysts, they enable simultaneous oxidation and reduction reactions, converting these pollutants into nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and water.
- Diesel Oxidation Catalysts (DOC): Specifically designed for diesel engines, DOCs primarily target hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide emissions. These converters use precious metal catalysts like platinum and palladium to promote oxidation reactions, reducing these pollutants to carbon dioxide and water.
- Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF): Unlike traditional catalytic converters, DPFs focus on capturing and reducing particulate matter emissions from diesel engines. They trap soot and particulates, allowing periodic regeneration to burn off the trapped particles, often aided by a catalyst coating.
- Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR): Commonly found in diesel vehicles, SCR systems reduce nitrogen oxides by using a urea-based solution, known as diesel exhaust fluid (DEF), in combination with a catalyst, typically composed of metals like platinum, palladium, or rhodium. This process converts NOx into nitrogen and water vapor.
Different types of catalytic converters operate uniquely, tailored to specific engine types and emission control requirements. Advances in materials and designs continue to enhance their efficiency and effectiveness in reducing harmful emissions, contributing to cleaner air, and meeting stringent environmental regulations worldwide. Hence, these devices are expensive and you can save on replacement costs via recycling.
How to Recycle My Catalytic Converter?
A clogged catalytic converter that came out of its lifespan still retains value. Recycling allows you to retrieve precious metals from the converter and establish exact price quotes for Pt, Pd, and Rh contains. Then you can sell it knowing the value of your specific converter. So here are 5 simple steps to do that:
- Identify catalytic converter
- Get the price
- Find a buyer company
- Ship it or had over
- Get paid
How to identify a catalytic converter?
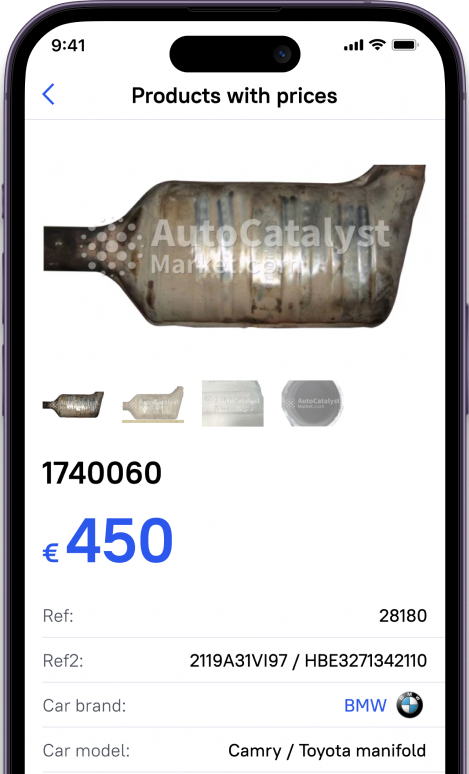
Identifying catalysts is possible via serial number, car brand, or manufacturer. All of these lookups are available on the AutoCatalystMarket website in specific tabs. Here you can also get the price along with the buyer company by selecting your region. As you have your catalyst identified and approximate the price, the buyer will take care of recycling, which in turn will present you with an exact price after the catalysts are refined in recycling. Therefore, you will get paid right after that.
In essence, online platforms like AutoCatalystMarket offer a convenient alternative to visiting local scrapyards, where prices may not be equitable, and illegal dealings with stolen catalysts are prevalent. On the other hand, the AutoCatalystMarket with reputable buyer companies and fair pricing, streamlines the selling process, ensuring a hassle-free experience while eliminating complexities associated with traditional methods.