- Preparation stage
- Definitions and Terms
- How to Separate the Metals in a Catalytic Converter
- How to Remove Palladium from a Catalytic Converter
- How to Extract Gold from Catalytic Converters
- How to get Rhodium out of a Catalytic Converter
- Wash-Dry-Refine
- Safety Considerations
- How to Earn on used Catalytic Converters
- Conclusion
Catalytic converters are not just components in your car's exhaust system, they are treasure troves of precious metals waiting to be reclaimed. These metals could be in various combinations, but mostly they include Platinum, Palladium, and Rhodium, and also may include other metals such as Gold. These metals form the cost of used catalysts. In this guide, we will explore how to get precious metals out of catalytic converters elaborating on the chemical reactions involved in extracting and separating these valuable metals effectively.
Preparation stage
Before getting into the intricacies of chemical processes to extract precious metals out of catalytic converter, we need to prepare it. This involves honeycomb extraction from the casing which contains all the metals inside. This is the initial stage of recycling catalytic converters. As you get this done, you need to grind the honeycomb into powder as the larger surface will be better at reacting with the chemicals during the extraction stages.
Definitions and Terms
At the heart of metal extraction lies a common methodology involving leaching, dissolution, and precipitation. While the process remains consistent, the choice of chemicals varies depending on the metal being targeted. Here are the short definitions for the terms:
- Leaching is dissolving the metals from the catalytic converter substrate using acidic solutions such as hydrochloric acid (HCl) and nitric acid (HNO₃).
- Dissolution - dissolving the metals into solution, enabling their extraction.
- Precipitation - The selective isolation of metals from the solution by causing them to form insoluble compounds.
These are similarities in the process, but each metal requires its own treatment to be extracted (precipitate) in its purity. Below, we explain what to apply to a solution to get specific metals out.
How to Separate the Metals in a Catalytic Converter
As we have our catalytic powder prepared, it is time to start the chemical process incorporating the above-mentioned treatments.
At first, we need to dissolve the powder into a solution. For that, put the material into a container and pour in a mixture of hydrochloric acid (HCl) and nitric acid (HNO₃), which act as potent solvents. This process is called leaching. Heat the solution gently to accelerate the leaching process and allow sufficient time for the metals to dissolve completely.
Then there comes a selective precipitation for each of the precious metals to extract from the solution.
How to Remove Palladium from a Catalytic Converter
To extract Palladium we need to selectively precipitate it from the solution. Such reagents as dimethylglyoxime (DMG) or ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl) are meant to selectively bind with ions of palladium in a solution which in turn forms a distinct precipitate. Now you can simply filter and wash it out to get rid of impurities and here you have your Palladium extracted.
How to Extract Gold from Catalytic Converters
Now, the same solution that we have extracted palladium from, we are going apply with reducing agents: sodium metabisulfite (Na₂S₂O₅) or oxalic acid. These agents facilitate the precipitation of gold, allowing it to separate from the solution in solid form. Filter the solid gold and put it aside for the moment right next to the palladium precipitant.
How to get Rhodium out of a Catalytic Converter
To separate Rhodium out of a solution it requires a complexation method before precipitation.
- Complexation: To be able to selectively recover Rhodium, we apply specific ligands or chelating agents like dimethylglyoxime or ammonium thiocyanate (NH₄SCN). These agents form complex compounds with rhodium ions, enabling their separation from the solution in the next step.
- Precipitation: Commonly used reagents for precipitating rhodium complexes include sodium borohydride (NaBH₄), ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl), or sodium hydroxide (NaOH). These reagents react with the rhodium ions present in the solution to form insoluble rhodium compounds, such as rhodium hydroxide or rhodium chloride. With this addition, you will start to see how rhodium compounds start forming and settle down, which you can then filter out the same as the previous metals.
- Filtering: Filter out the solid Rhodium out of the solution and put the filtered metal aside.
Wash-Dry-Refine
Here we have our 3 metals separated in a solid form and they mostly look like powders at the moment. Wash each of them separately with distilled water to get rid of impurities. Let them dry after washing. To refine, we need to have a blast furnace or any other way to melt these compounds separately. Blasting will refine and give metals their original look.
Safety Considerations
This guide is meant to describe the recycling processes that are done in the factory. It is not recommended to DIY at home. Some of the mentioned chemicals may not be available to get. Moreover, chemicals such as acidic solutions and other reagents used in the extraction process require adequate ventilation and personal protective equipment including gloves and goggles to minimize the risk of accidents or injuries. Besides, appropriate disposal of chemical waste is mandatory afterward.
How to Earn on used Catalytic Converters
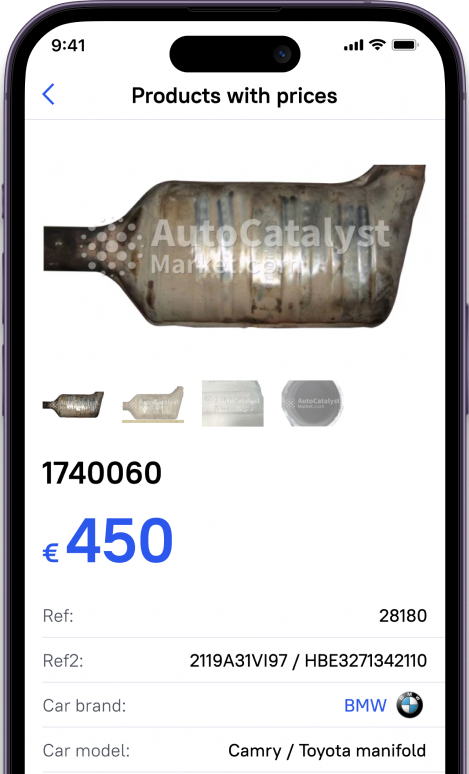
If you want to earn from your worn-out cat, you can use the AutoCatalystMarket website where you easily get a price list for your catalysts by serial numbers. The site provides all the needed resources to sell used catalytic converters including reputable buyers bound to your region. The buyer company will carry out all the complexities regarding recycling and refining precious metals from the converter and give you a fair price.
Conclusion
Now you know how to get the metals out of a catalytic converter. This is what happens in the recycling stages when you sell your catalysts. This usually involves XRF analysis to estimate the precious metals content before extraction and the real value comes out after leaching, refining, and blast furnace treatments. Recycling is meant to retrieve such valuable resources as Pt, Pd, and Rhodium which in turn contributes both to environmental protection and economic sustainability.