- Special linings in a catalyst
- Some factors affect the cost and platinum contents:
- Selling Your Catalytic Converter for Precious Metals
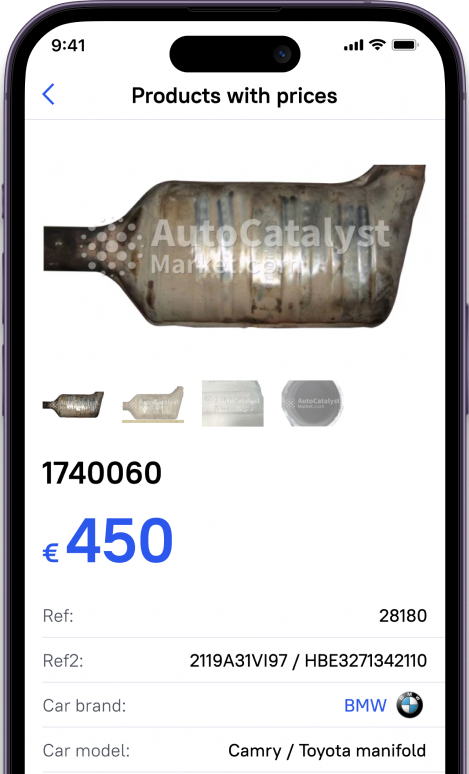
A platinum catalyst is used in many vehicles today. It is one of the main elements of the exhaust system and reduces harmful emissions. Catalyst's body is plated with precious metals, which, under certain conditions, can be extracted. However, it is difficult to predict in advance how much platinum is contained in a car catalyst.
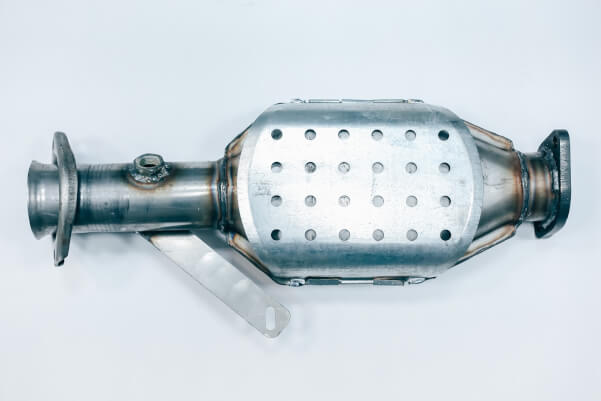
The fundamental design of catalysts has hardly changed since its inception, which cannot be said about manufacturing technologies. In recent years, thermal and aerodynamic performance has been particularly improved, resulting in improved neutralization and long-term stability. The main parts of every catalyst are housing and exhaust system made of stainless steel (expensive materials); special pads (protection and fixation for the ceramic block); support material or block (metal or ceramic); intermediate fixing layer for precious metals; catalytically active layer.
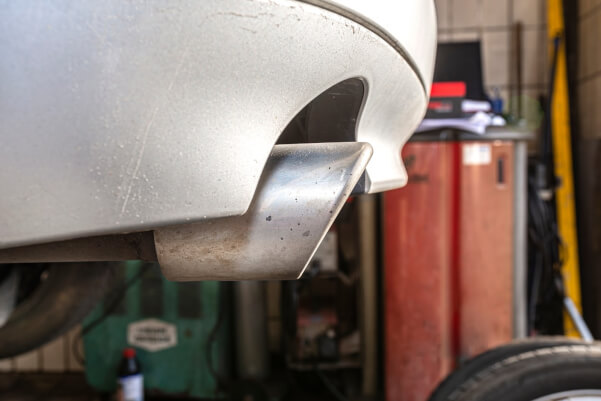
The stainless steel body of a catalyst
A stainless steel housing is required to provide good corrosion protection against water formation during the neutralization of harmful components. This is the only way to ensure a catalyst sufficient service life of at least 3-5 years. The material used is chromium or nichrome steel, which is resistant to corrosion, acids, and heat.
Special linings in a catalyst
They serve to fix the ceramic block and compensate for the thermal expansion of a ceramic block and stainless steel housing. Also, they dampen vibrations, absorb mechanical loads and axial and radial accelerations. The pads consist of a special wire mesh or ceramic fiber with an insert of mica plates. Due to the interweaving of mica plates, the pads expand under the influence of temperature and adapt to the gap between the block and the stainless steel case.
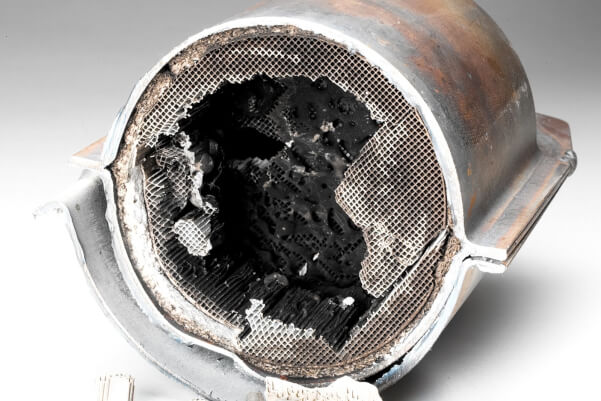
The interior of the automotive catalyst is filled with a special structure made of ceramics or metal. Outwardly, it resembles a honeycomb. The top of a catalyst is coated with a thin layer of precious metal.
The presence of such spraying ensures a reduction in the level of harmful emissions. This is achieved because exhaust gases, in contact with precious metals like platinum, rhodium, and palladium, and other substances, enter into a chemical reaction with them.
Each of these metals is highly rated. Therefore, automotive catalysts attract many people who are involved in the extraction of precious materials for further resale.
For many years, platinum has been the most valuable metal in a catalyst. There were times when it cost five times as much as palladium. But since 2015, the production of diesel vehicles has dropped significantly. This triggered a drop in platinum prices. If earlier this metal cost $ 2.2 thousand per ounce (about 31.1 grams), then in recent years it has been estimated at $ 600-800. In turn, precious metals used in gasoline cars have risen in price. Thus, the prices for rhodium in recent years have grown from 1.5 thousand to 12 thousand dollars per ounce.
Seeing such impressive numbers, many would want to know how many of these metals are contained in one automotive catalyst? It all depends on the car, its engine, and especially the market for every model. One car with the same engine could have different catalysts for different countries. If we calculate the "average", platinum in one catalyst is approximately one and a half grams per kilogram, palladium - 1.3-1.4 g / kg, rhodium - 0.15 g / kg. The knocked-out catalyst weighs about 1.2 kilograms.
The extraction of these metals from a catalyst is a rather complicated process that requires the availability of appropriate skills and various expensive substances. There are several technologies through which precious metals can be extracted. The choice in favor of a particular technology is mainly determined by the capabilities of a person who obtains platinum from a catalyst. It is also important to understand that there are inevitable losses of recoverable materials during the refining process. In particular, such disadvantages are noted in the leaching technique, which requires multiple washing of chemical reaction components.
The surface of the catalysts is coated with precious metals. These materials can be retrieved with appropriate skills and reagents.
Some factors affect the cost and platinum contents:
1. Catalyst price depends on which sales market a particular car was originally assembled for. Higher quality catalysts are supplied to European markets than to third world countries.
2. A higher class of a car guarantees better catalytic converters.
3. The longer service life of a car decreases precious metals.
4. Sports driving helps to "empty" catalytic converter more quickly.
5. Fuel. Certain fuel additives leach metals from catalysts.
6. There are catalysts with different compositions of precious metals:
6.1. Pt, Pd + Rh - "classic" and the oldest type of catalytic converter. Average content per one ton of ceramics (ppm): Pt - 1470, Pd - 900, Rh - 270. Today, it is already an “endangered” species.
The average price for this category: 50-60 EUR / kg.
6.2. Pt + Rh - usual catalysts from diesel or premium cars.
These catalysts lack palladium, but platinum is in order of 2500-3500 ppm. The cost of this category of catalysts is 65-75 euro/kg.
6.3 Pd + Rh - Platinum is absent, but palladium is of an order of 3000-3500 ppm. Such catalysts make up about 70% of the total amount of modern catalytic converters.
Average price 45-55 euros / kg.
From the above, we can conclude that it is impossible to determine the cost of a catalyst without analysis!
Selling Your Catalytic Converter for Precious Metals
Experienced professionals know both manufacturers and even models, catalytic converters of which contain the greatest amount of precious metals. For example, diesel cars use platinum, gasoline cars use palladium. Hybrid vehicles have higher palladium content than conventional vehicles.
This is since hybrids do not have time to warm up catalyst to increase its efficiency, so more metal is required to absorb more harmful emissions.
Most car owners simply sell catalysts for precious metals, rather than selling them as spare parts. The mass of palladium contained in a "honeycomb" of one catalyst can reach 1.5-2 grams. Considering that some premium cars use paired catalysts, the income from one car can reach a good sum of money.
For example, one well-known German manufacturer contains platinum (0.12% by weight), palladium (0.08% by weight), and rhodium (0.008% by weight) in the composition of a catalyst weighing 1200 grams.
The problem is that this palladium from the alloy still needs to be isolated somehow. There are several ways and all of them are quite expensive and complicated, so there is absolutely no point in working with single instances.
At the moment, the largest automakers are trying to stock up on catalyst palladium for future use, since the price for it, according to all forecasts, will only grow. But this growth cannot be endless. It will last exactly as long as it is more profitable and more efficient to use another metal - platinum. Already, it is more than half the price of palladium.
You can contact our Buyers to sell a scrap catalytic converter.Nevertheless, the very transition of catalyst from one metal to another is not possible in a short time, the restructuring of production can take several years and many billions of euros. That is why one of the most expensive items in the budget of many large automakers has become the search for replacements for palladium and platinum. Eco-friendliness of cars should be cheaper.