- What is Rhodium?
- Role of Rhodium in Catalytic Converters
- How much Rhodium is in a Catalytic Converter in Grams
- Factors Affecting Rhodium Content
- Impact of Rhodium Price Changes on Converter Value
- How to Get Rhodium out of a Catalytic Converter?
- Which catalytic converters have the most rhodium?
- How to sell my catalytic converter?
Catalytic converters, integral components within vehicular exhaust systems, harness a synergy of precious metals – platinum, palladium, and notably, rhodium. Amid their collective efficacy in mitigating harmful emissions, rhodium emerges as a focal point of discussion for its pivotal role. This discourse aims to navigate the realm of catalytic converters, meticulously examining the paramount significance of rhodium and its consequential presence in these automotive catalysts.
What is Rhodium?
Rhodium, a transition metal denoted by atomic number 45 in the periodic table, embodies a spectrum of chemical traits distinguishing it among elements. Renowned for its resilience and remarkable corrosion resistance, rhodium boasts a lustrous, silver-white hue, forming compounds with diverse oxidation states. Among the rarest and expensive elements on Earth, its scarcity in the Earth's crust presents a considerable challenge in extraction. Now, where is rhodium found in scrap? Its primary sources reside within platinum or nickel ores, necessitating complex extraction procedures involving precise chemical reactions and meticulous purification processes. Rhodium's rarity and unique chemical properties render it not just a precious metal but an elusive and coveted element within various industries beyond automotive catalysis, including jewelry, electronics, and specialized chemical applications.
Role of Rhodium in Catalytic Converters
Rhodium assumes a core role in catalytic converters, leveraging its exceptional catalytic properties to accelerate chemical reactions crucial in transforming harmful pollutants into less harmful compounds. As a catalyst a substance expediting reactions without undergoing permanent alteration – rhodium facilitates the conversion of toxic gases like nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons into less harmful substances like nitrogen, water vapor, and carbon dioxide. Its unique ability to withstand high temperatures and efficiently catalyze these reactions, especially in the reduction of nitrogen oxides, makes it indispensable in these emission-control devices. The precision and efficiency with which rhodium drives these chemical transformations underscore its indispensability within catalytic converters, playing a vital part in curbing vehicular emissions.
How much Rhodium is in a Catalytic Converter in Grams
So, how many ounces of Rhodium in a catalytic converter? The quantity and weight of rhodium in a catalytic converter varies based on its specific design and composition. Typically, the converters contain less rhodium than other precious metals like platinum and palladium. On average, a catalytic converter might contain anywhere from 2 to 6 grams (0,07- 0,2 ounces) of rhodium, but this quantity can fluctuate. Advanced converter designs aim for more efficient usage of rhodium, utilizing as little as possible without compromising the catalytic performance. The optimization of rhodium content reflects an intricate balance between economic feasibility and achieving optimal emission reduction, ensuring the converter's functionality while conserving this scarce and valuable element.
Factors Affecting Rhodium Content
The rhodium content in catalytic converters is intricately influenced by multifaceted factors – Euro standards, crucial in shaping emission regulations, significantly impact converter designs. For instance, Euro 6 standards necessitate advanced catalytic systems, like Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR), requiring less rhodium due to efficient nitrogen oxide reduction. Converter types, such as those employing ceramic honeycomb structures, play a vital role. Three-way catalysts (TWC), often utilizing ceramic honeycomb substrates, demand more rhodium for their broader emission reduction scope compared to diesel oxidation catalysts (DOC) or diesel particulate filters (DPF). Engine advancements and varying fuel qualities further alter rhodium needs, demanding tailored converter designs. Additionally, recycling initiatives and supply chain shifts markedly affect rhodium availability, influencing its usage in converters.
Impact of Rhodium Price Changes on Converter Value
Fluctuating rhodium scrap prices significantly impact the value of catalytic converters. Rhodium's scarcity and price volatility directly shape a converter's worth. High rhodium prices inflate the value of converters rich in this metal, attracting interest from recyclers and buyers. Conversely, price dips proportionally reduce converter value.
Beyond individual valuation, these price changes reverberate across industries reliant on converters. Automotive and recycling sectors feel these effects, with higher rhodium prices potentially impacting new vehicle production costs including the catalytic converters and consumer pricing. Conversely, reduced rhodium costs may alleviate manufacturing expenses, influencing market dynamics. The interplay between rhodium prices and converter values underscores the need to track these fluctuations for stakeholders. The precious metal exchange markets also play a pivotal role. Exchange market shifts affect rhodium pricing, cascading effects onto converter values and industry dynamics. Understanding these markets aids in gauging converter worth amid fluctuating rhodium prices, and steering decisions in the automotive and recycling sectors.
Monitoring rhodium prices via our AutoCatalystMarket website is vital, providing real-time precious metal price tracking, including rhodium rates. This resource empowers informed decisions about overall catalytic converter value, specific quotes, manufacturers, and car brands. The site counts over 25,000 units with an image library of 50,000 pictures that help to identify your catalyst.
How to Get Rhodium out of a Catalytic Converter?
Rhodium extraction embodies recycling, an intricate process essential in reclaiming valuable elements. This multifaceted procedure involves distinct stages:
- Decanning: Removing the converter's shell.
- Grinding: Reducing the catalyst to a fine powder.
- Acid Digestion: Dissolving the powder using acids like aqua regia.
- Precipitation: Isolating rhodium compounds.
- Filtering: Separating the precipitate for purification.
- Reduction: Converting compounds into metallic rhodium.
- Smelting: Melting the refined rhodium.
- Final Refinement: Ensuring high-purity rhodium.
The refined rhodium continues the sustainability cycle, either finding use in new converters or contributing to the market supply. Recycling catalytic converters, especially for their rhodium content, not only conserves valuable metals but also significantly reduces environmental impact—an exemplary practice of sustainable resource utilization.
Which catalytic converters have the most rhodium?
Three-way catalysts (TWC), found in catalytic converters of gasoline-powered vehicles across various car brands like Toyota, Honda, or Volkswagen, commonly boast the highest rhodium content. These converters require a fine-tuned balance of rhodium, platinum, and palladium to efficiently control emissions. For instance, in some Toyota models equipped with TWCs, the catalytic converters may contain higher proportions of rhodium due to their comprehensive emissions reduction capabilities, crucial for meeting stringent environmental standards. While diesel vehicles from manufacturers like Ford or Mercedes-Benz rely on different emission control mechanisms such as diesel oxidation catalysts (DOC) or diesel particulate filters (DPF), they generally contain lower rhodium amounts compared to gasoline vehicle converters.
How to sell my catalytic converter?
There are two primary ways to sell a used catalytic converter. The traditional approach involves scrapyards, presenting both advantages and drawbacks. Accessibility stands as a key benefit, especially if a scrapyard is nearby. However, scrapyards are associated with illegal activities involving stolen catalysts, and they often offer lower prices.
Alternatively, a more advantageous method is leveraging online platforms like AutoCatalystMarket. This approach connects sellers with trustworthy buyer companies, ensuring fair deals and eliminating the risks associated with scrapyards. Notably, the online platform maintains accessibility by allowing sellers to select regional dealers tailored to their sales.
To sell your catalyst on AutoCatalystMarket, follow these steps:
- Prepare Your Catalyst: Ensure the converter is ready for sale by removing excess pipes and ensuring it's ready for shipment.
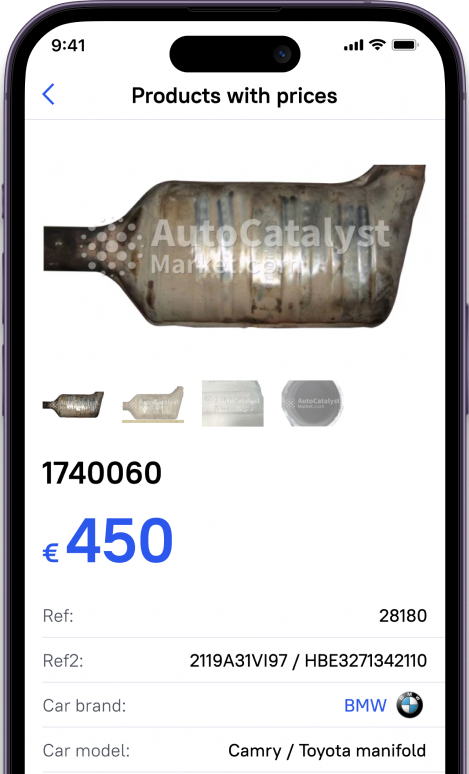
- Get a Quote: Contact potential buyers for an accurate price based on serial numbers or images.
- Shipping (Optional): If shipping, securely package the converter to prevent damage during transit.
- Payout: Once the buyer confirms the converter's value upon receipt, expect payment for your sale.
Make the most of AutoCatalystMarket to streamline your selling process. Simplify every step, from converter preparation all the way to securing your payment.